Application Management Layer
The Application Management Layer (AML) is a comprehensive package that provides classes and workflows for managing AI models, applications and workloads, facilitating interaction between various IT professionals such as DevOps Engineers, Application Developers, Data Engineers, and Data Scientists.
The package documentation elaborates on the Application Management Layer (AML) which forms an important component in managing complex workflows and applications through the application development lifecycle.
Based on the identified use cases, the AML contains key functionalities for managing AI models, applications, and workloads. IT professionals such as DevOps engineers, application developers, data engineers, and data scientists are the primary actors who interact with the AML, utilizing different methods to perform distinct use cases.
The use case ‘Manage AI Models’ outlines how a Data Scientist manages AI models in coordination with DevOps to ensure that both the AI models and applications are updated together. The scenarios within this use case cover actions like creating, deploying, destroying, and updating AI models.
In the ‘Manage Applications’ use case, DevOps Engineers and Application Developers collaborate to manage applications across multiple platforms. The operations within this use case include building, creating, deploying, destroying, monitoring, and updating the applications.
The use case ‘Manage Workloads’ enables Application Developers to interconnect applications through workflows, thereby automating complex data interactions between various applications across a hybrid infrastructure. The included operations are creating, deploying, destroying, monitoring, and updating the workloads.
Within the AML package, we have several key classes including Application, Application Instance, Application Template, Workload, Workload Instance, and Workload Template. Each of these classes provides methods for managing their instances, including operations like creating, destroying, adding to, updating, and removing from the instances.
Furthermore, there are defined workflows for managing AI models, applications, and workloads. These workflows illustrate the sequential actions, conditions, and transitions between different states for each operation, specifying the actors responsible for each action and the outcome of their activities.
Overall, the AML provides a comprehensive management system for AI models, applications, and workloads, connecting different users and their actions in an organized, modular manner.
Use Cases
The following are the use cases of the Application Management Layer subsystem. Each use case has primary and secondary scenarios that are elaborated in the use case descriptions.
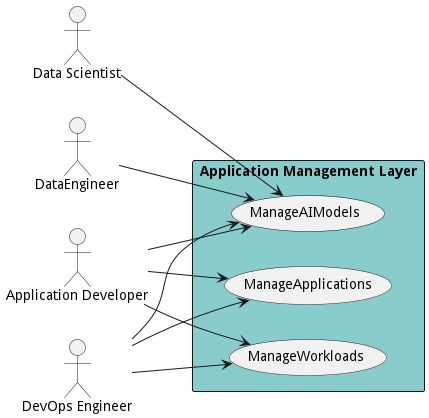
Users
The following are the actors of the Application Management Layer subsystem. This can include people, other subsystems inside the solution and even external subsystems.
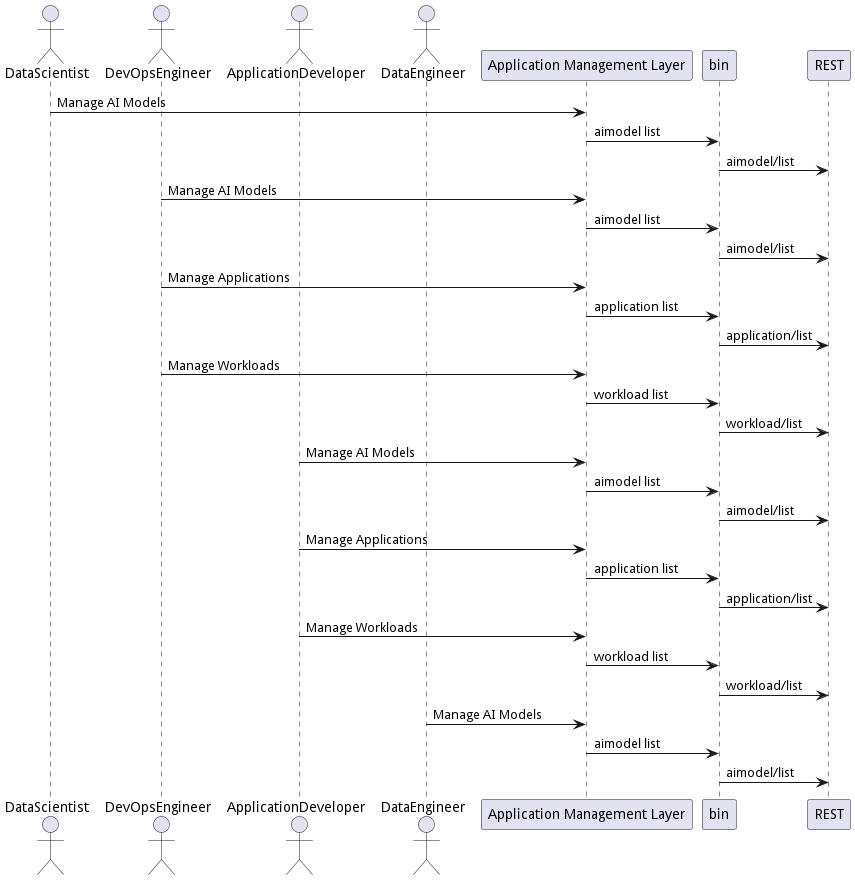
Interface
The subsystem has a REST, CLI, WebSocket, and Web interface. Use Cases and Scenarios can use any or all of the interfaces to perform the work that needs to be completed. The following diagram shows how users interact with the system.
- edgemere aml aimodel create
- edgemere aml aimodel deploy
- edgemere aml aimodel destroy
- edgemere aml aimodel list
- edgemere aml aimodel scan
- edgemere aml aimodel sign
- edgemere aml aimodel update
- edgemere aml aimodel validate
- edgemere aml application create
- edgemere aml application deploy
- edgemere aml application destroy
- edgemere aml application list
- edgemere aml application monitor
- edgemere aml application update
- edgemere aml data create
- edgemere aml workload create
- edgemere aml workload deploy
- edgemere aml workload destroy
- edgemere aml workload list
- edgemere aml workload monitor
- edgemere aml workload update
Logical Artifacts
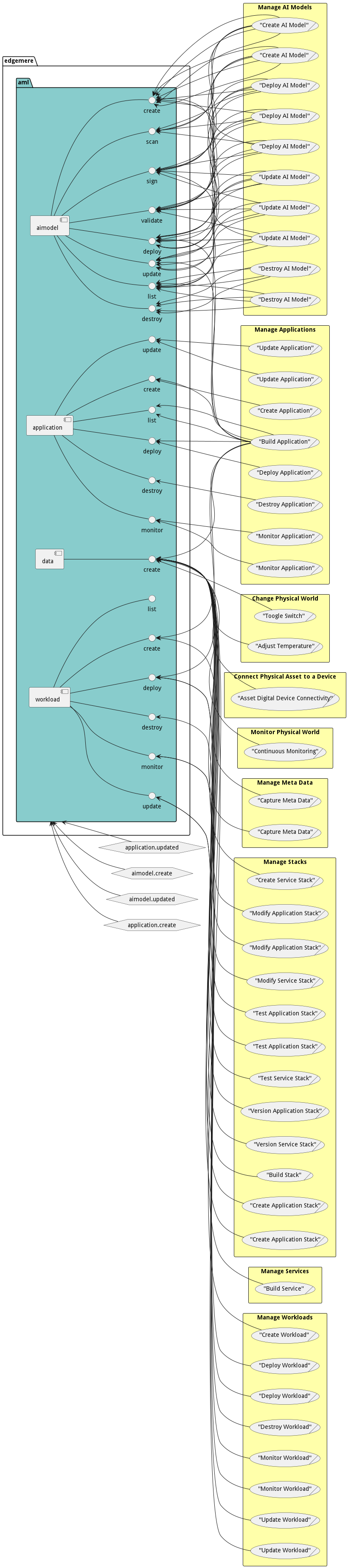
The Data Model for the Application Management Layer subsystem shows how the different objects and classes of object interact and their structure.
Sub Packages
The Application Management Layer subsystem has sub packages as well. These subsystems are logical components to better organize the architecture and make it easier to analyze, understand, design, and implement.
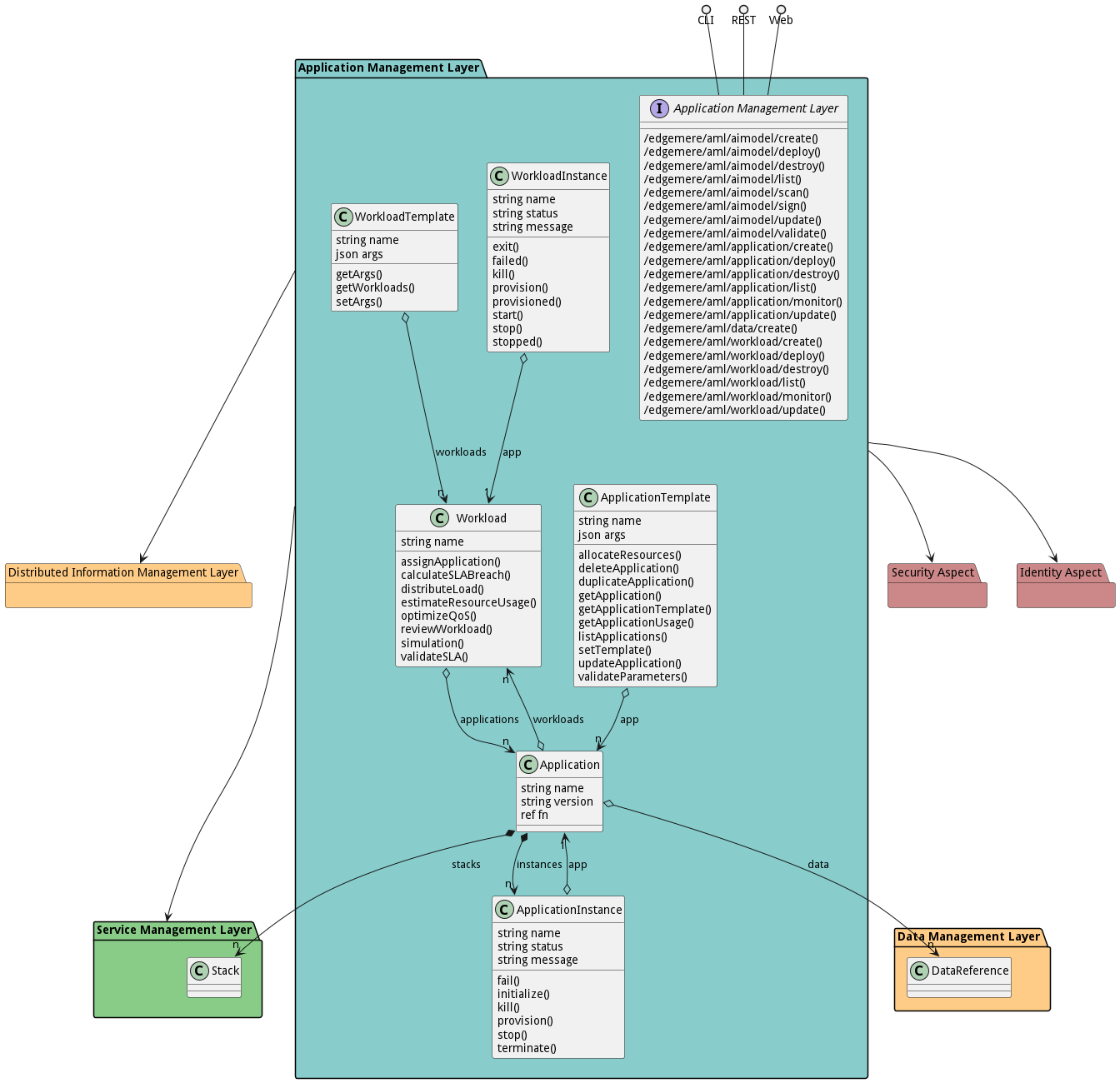
Classes
The following are the classes in the data model of the Application Management Layer subsystem.
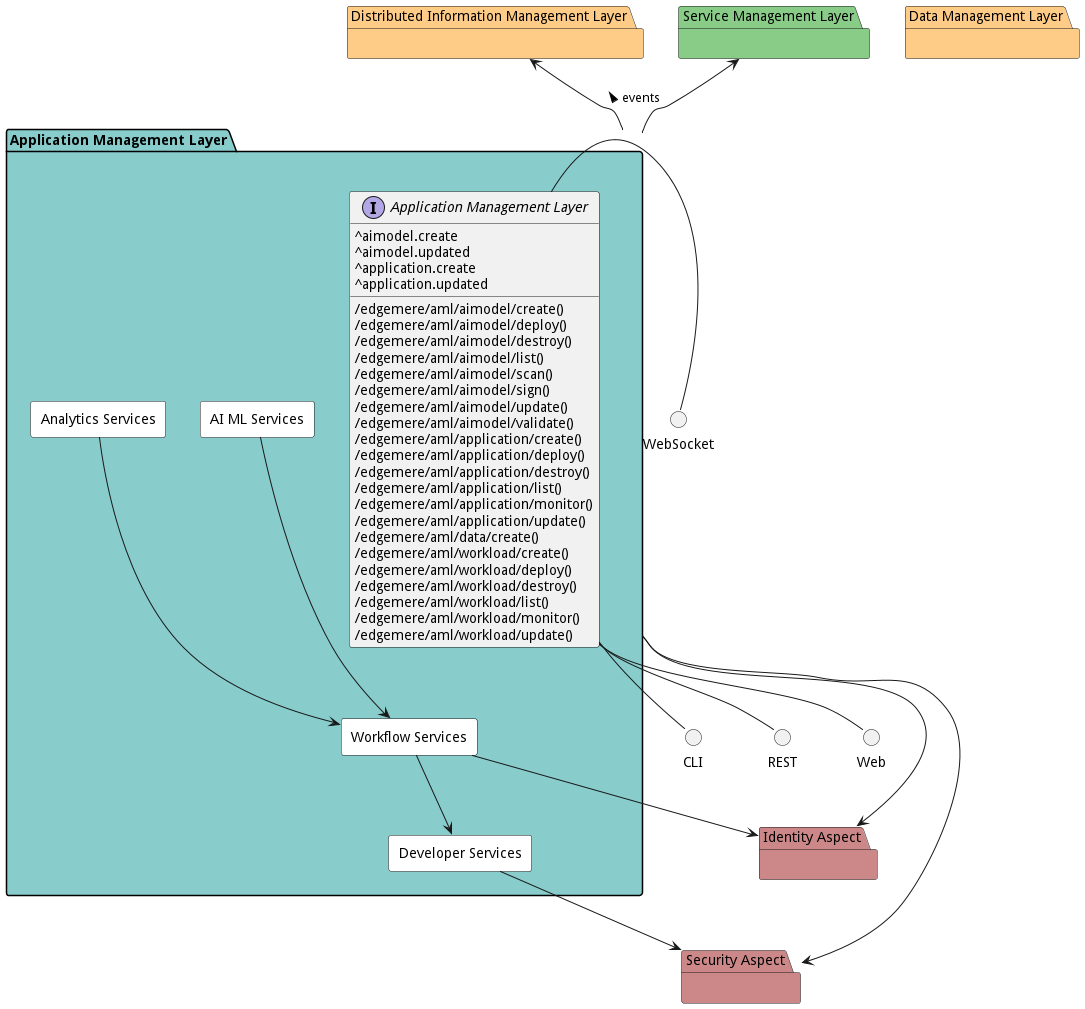
Deployment Architecture
This subsystem is deployed using micro-services as shown in the diagram below. The ‘micro’ module is used to implement the micro-services in the system. The subsystem also has an CLI, REST and Web Interface exposed through a nodejs application. The nodejs application will interface with the micro-services and can monitor and drive work-flows through the mesh of micro-services. The deployment of the subsystem is dependent on the environment it is deployed. This subsystem has the following environments:
Physical Architecture
The Application Management Layer subsystem is physically laid out on a hybrid cloud infrastructure. Each microservice belongs to a secure micro-segmented network. All of the micro-services communicate to each other and the main app through a REST interface. A Command Line Interface (CLI), REST or Web User interface for the app is how other subsystems or actors interact. Requests are forwarded to micro-services through the REST interface of each micro-service. The subsystem has the a unique layout based on the environment the physical space. The following are the environments for this subsystems.
Micro-Services
These are the micro-services for the subsystem. The combination of the micro-services help implement the subsystem’s logic.
dev
Detail information for the dev environment can be found here
Services in the dev environment
- aml_web : aml_web
- aml_as : aml_as
- aml_ds : aml_ds
- aml_ws : aml_ws
- aml_ams : aml_ams
test
Detail information for the test environment can be found here
Services in the test environment
- aml_web : aml_web
- aml_as : aml_as
- aml_ds : aml_ds
- aml_ws : aml_ws
- aml_ams : aml_ams
prod
Detail information for the prod environment can be found here
Services in the prod environment
- aml_web : aml_web
- aml_as : aml_as
- aml_ds : aml_ds
- aml_ws : aml_ws
- aml_ams : aml_ams
Activities and Flows
The Application Management Layer subsystem provides the following activities and flows that help satisfy the use cases and scenarios of the subsystem.
Messages Handled
The Application Management Layer subsystem is an event driven architecture and handle several events. The following events are handled by this subsystem. Please note that this subsystem is not the only subsystem that handles these events.
| Message | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| aimodel.create | Custom Action | |
| aimodel.updated | Custom Action | |
| application.create | Custom Action | |
| application.updated | Custom Action |
Messages Sent
| Event | Description | Emitter |
|---|---|---|
| application.create | When an object of type Application is created. | Application |
| application.destroy | When an object of type Application is destroyed. | Application |
| application.updated | When an object of type Application has an attribute or association updated. | Application |
| applicationinstance.create | When an object of type ApplicationInstance is created. | ApplicationInstance |
| applicationinstance.destroy | When an object of type ApplicationInstance is destroyed. | ApplicationInstance |
| applicationinstance.updated | When an object of type ApplicationInstance has an attribute or association updated. | ApplicationInstance |
| applicationtemplate.create | When an object of type ApplicationTemplate is created. | ApplicationTemplate |
| applicationtemplate.destroy | When an object of type ApplicationTemplate is destroyed. | ApplicationTemplate |
| applicationtemplate.updated | When an object of type ApplicationTemplate has an attribute or association updated. | ApplicationTemplate |
| workload.create | When an object of type Workload is created. | Workload |
| workload.destroy | When an object of type Workload is destroyed. | Workload |
| workload.updated | When an object of type Workload has an attribute or association updated. | Workload |
| workloadinstance.create | When an object of type WorkloadInstance is created. | WorkloadInstance |
| workloadinstance.destroy | When an object of type WorkloadInstance is destroyed. | WorkloadInstance |
| workloadinstance.updated | When an object of type WorkloadInstance has an attribute or association updated. | WorkloadInstance |
| workloadtemplate.create | When an object of type WorkloadTemplate is created. | WorkloadTemplate |
| workloadtemplate.destroy | When an object of type WorkloadTemplate is destroyed. | WorkloadTemplate |
| workloadtemplate.updated | When an object of type WorkloadTemplate has an attribute or association updated. | WorkloadTemplate |
Interface Details
The Application Management Layer subsystem has a well defined interface. This interface can be accessed using a command line interface (CLI), REST interface, and Web user interface. This interface is how all other subsystems and actors can access the system.
Action edgemere aml aimodel create
- REST - /edgemere/aml/aimodel/create?
- bin - edgemere aml aimodel create
- js - .edgemere.aml.aimodel.create({ })
Description
Creates a new AI model
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml aimodel deploy
- REST - /edgemere/aml/aimodel/deploy?
- bin - edgemere aml aimodel deploy
- js - .edgemere.aml.aimodel.deploy({ })
Description
Deploys a specified AI model
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml aimodel destroy
- REST - /edgemere/aml/aimodel/destroy?
- bin - edgemere aml aimodel destroy
- js - .edgemere.aml.aimodel.destroy({ })
Description
Destroys a specified AI model
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml aimodel list
- REST - /edgemere/aml/aimodel/list?
- bin - edgemere aml aimodel list
- js - .edgemere.aml.aimodel.list({ })
Description
Returns a list of AI models
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml aimodel scan
- REST - /edgemere/aml/aimodel/scan?appName=string
- bin - edgemere aml aimodel scan –appName string
- js - .edgemere.aml.aimodel.scan({ appName:string })
Description
An interface designed to scan the AI model for potential malware or viruses.
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| appName | string | The name of the AI model to scan. |
Action edgemere aml aimodel sign
- REST - /edgemere/aml/aimodel/sign?appName=string
- bin - edgemere aml aimodel sign –appName string
- js - .edgemere.aml.aimodel.sign({ appName:string })
Description
This interface is used to add a digital signature to the AI model to confirm its authenticity.
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| appName | string | The name of the AI model that needs to be digitally signed. |
Action edgemere aml aimodel update
- REST - /edgemere/aml/aimodel/update?
- bin - edgemere aml aimodel update
- js - .edgemere.aml.aimodel.update({ })
Description
Updates a specified AI model
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml aimodel validate
- REST - /edgemere/aml/aimodel/validate?appName=string&SLA=string
- bin - edgemere aml aimodel validate –appName string –SLA string
- js - .edgemere.aml.aimodel.validate({ appName:string,SLA:string })
Description
An interface to validate AI model based on SLA Pass Rate
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| appName | string | The unique identifier for the AI model to be validated. | |
| SLA | string | The Service Level Agreement details defining the expected performance and pass rates for the AI model |
Action edgemere aml application create
- REST - /edgemere/aml/application/create?
- bin - edgemere aml application create
- js - .edgemere.aml.application.create({ })
Description
Creates a new application
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml application deploy
- REST - /edgemere/aml/application/deploy?
- bin - edgemere aml application deploy
- js - .edgemere.aml.application.deploy({ })
Description
Deploys a specified application
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml application destroy
- REST - /edgemere/aml/application/destroy?
- bin - edgemere aml application destroy
- js - .edgemere.aml.application.destroy({ })
Description
Destroys a specified application
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml application list
- REST - /edgemere/aml/application/list?
- bin - edgemere aml application list
- js - .edgemere.aml.application.list({ })
Description
Returns a list of applications
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml application monitor
- REST - /edgemere/aml/application/monitor?attr1=string
- bin - edgemere aml application monitor –attr1 string
- js - .edgemere.aml.application.monitor({ attr1:string })
Description
Description of the action
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| attr1 | string | false | Description for the parameter |
Action edgemere aml application update
- REST - /edgemere/aml/application/update?
- bin - edgemere aml application update
- js - .edgemere.aml.application.update({ })
Description
Updates a specified application
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml data create
- REST - /edgemere/aml/data/create?attr1=string
- bin - edgemere aml data create –attr1 string
- js - .edgemere.aml.data.create({ attr1:string })
Description
Description of the action
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| attr1 | string | false | Description for the parameter |
Action edgemere aml workload create
- REST - /edgemere/aml/workload/create?
- bin - edgemere aml workload create
- js - .edgemere.aml.workload.create({ })
Description
Creates a new workload
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml workload deploy
- REST - /edgemere/aml/workload/deploy?
- bin - edgemere aml workload deploy
- js - .edgemere.aml.workload.deploy({ })
Description
Deploys a specified workload
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml workload destroy
- REST - /edgemere/aml/workload/destroy?
- bin - edgemere aml workload destroy
- js - .edgemere.aml.workload.destroy({ })
Description
Destroys a specified workload
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml workload list
- REST - /edgemere/aml/workload/list?
- bin - edgemere aml workload list
- js - .edgemere.aml.workload.list({ })
Description
Returns a list of workloads
Parameters
No parameters
Action edgemere aml workload monitor
- REST - /edgemere/aml/workload/monitor?attr1=string
- bin - edgemere aml workload monitor –attr1 string
- js - .edgemere.aml.workload.monitor({ attr1:string })
Description
Description of the action
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| attr1 | string | false | Description for the parameter |
Action edgemere aml workload update
- REST - /edgemere/aml/workload/update?
- bin - edgemere aml workload update
- js - .edgemere.aml.workload.update({ })
Description
Updates a specified workload
Parameters
No parameters