Action
An Action is something that an actor can perform on the system. It is implemneted such that an actor can interface with a CLI, REST or Web Interface.
Command Line Interface
# Create a interface action for MyPackage
ailtire action create --name "actionname" --package "MyPackage"
# Generates api/MyPackage/interface/actioname.js
# Create a method action for MyClass
ailtire action create --name "actionname" --model "MyClass"
# Generates api/MyPackage/models/MyClass/actioname.js
See ailtire action create for more information.
Generated Artifacts
Actions are implemented with a single javascript file. A REST, CLI, and Web Interface is automatically accessible by defining the action. Actions can be stored in the interface directory of the package or in the directory of the model of a package.
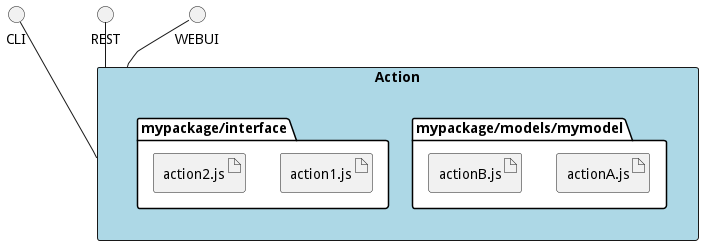
All actions are created following the template below.
module.exports = {
friendlyName: 'actionname',
description: 'Description of the action',
static: false, // True is for Class methods. False is for object based.
inputs: { // These are the parameters of the action.
name: {
description: 'Name of the object',
type: 'string', // string|boolean|number|json|object
required: true
},
param1: {
description: 'Parameter 1 of the action.'
type: 'object', // string|boolean|number|json|object
required: false
},
},
exits: {
success: (retval) => {
return retval;
},
json: (retval) => {
return {id:retval.id}
},
notFound: (inputs) => {
return {message: "Object Not found with name:", inputs.name}
}
},
fn: function (obj, inputs, env) { // Function to run when the action is called.
// Obj contains the object that the action is called for.
// Or the class if the action is static.
// Inputs contains a map of all of the inputs of action.
// env contains the environmen that the action was performed.
let item = Object.find(inputs.name);
if(!item) {
throw new Error({type:'notFound', inputs: inputs});
}
return item;
}
};
Action definition
friendlyName
Name that action is called. All action can be called through different ways.
Description
Description of the action. This is used in the documentation generation of the architecture.
static
Static is true if this is a class method for model actions. Always static for package interface actions.
inputs
These are the parameters of the action. The inputs attribute is a map that maps the parameters by name. Each input has the following attributes:
- description - description of the parameter. USed for documentaiton and command line help command.
- type - This is the type of parameter ( string, boolean, number, json, or object).
- required - true or false. Throw an except if required parameter is not submitted.
exits
The exits are called when the function exits.
- success - return to the calling function or AService.call to the action. The parameter passed in is what was returned from the fn.
- json - This is called when the env.res has been set and will package up the return value from the fn (passed into the json function as retval). What ever is returned from here will sent via env.res.json call over the rest interface.
- notFound - This is an error type that is called when an Error is throw with the parameter type set to ‘notFound’
Additional exit types can be added to handle different types of errors or return types as defined by the type in the Error constructor.
fn
This if the function that will be called when the action is fired. The function has three paramters.
- obj - Object of the function if static is false and the action is for a model.
- inputs - Contains a map of the inputs passed into the action.
- env - Contains the calling environment of the action. If REST contains env.req and env.res variables.
Calling the Action
The action can be called using several different techniques.
- javascript
- CLI - command line interface
- REST - REST interface
- Web UI - Web User Interface
Package Interface (Action)
This shows how actions for a package are accessed in javascript, cli, rest and web interface.
javascript
The package interface can be called within a javascript.
let results = AService.call('mypackage.actionname', {param1: 'name1'}, {param2: 'name2')};
Command Line Interface (CLI)
The package interface can be called with the command line interface.
# Name of the paplication is myapp
myapp mypackage actionanem --param1 name1 --param2 name2
REST
The package interface can be called with the REST inteface.
# Name of the paplication is myapp
curl "http://localhost:8080/mypackage/actionname?param1=name1¶m2=name2"
Web Interface
Look at the left panel for in the web interface under the packages items.
Model Action
Each Model has standard actions that are automatically generated.
- create
- list
- show
- update
This shows how actions for a model are accessed in javascript, cli, rest and web interface.
javascript
The model action can be called within a javascript. Both static and object are shown.
let obj = MyModel.create({name:'myModel'}); // Static method.
obj.myaction({param1: name1, param2: name2}); // Object Method.
Command Line Interface (CLI)
The model action can be called with the command line interface.
myapp mymodel create --name myName # Static call
myapp mymodel actionanem --id obj_id --param1 name1 --param2 name2 # Object call
REST
The model action can be called with the REST inteface.
# Static Call
curl "http://localhost:8080/mymodel/create?name=myname"
# Object Call
curl "http://localhost:8080/mymodel/actioname?param1=name1¶m2=name2"
Web Interface
Look at the right panel for in the web interface under the packages items.